
Progesterone-only Methods of Contraception

Types:

Depo-Provera

Progestogen-only pill (POP)

Implants

Intrauterine system (IUS)
In this module, we will only discuss POP and Depo-Provera. IUS will be discussed in a separate module, please see "LARC".
Progestogen-only Pill (POP)
-
Types of POPs are available:
-
Traditional POPs
-
eg: Noriday (Norethisterone- NET), Microlut (Levonorgestrel-LNG)
-
-
Contain small doses of synthetic progesterone with no estrogen.
-
Both contain 28 pills in a packet and are taken continuously with no pill-free period.
-
Typical use Failure Rate is 9%.
-
No delay in fertility return following the discontinuation.
-
Safe in patients with migraine.
-
No association with headache, cardiovascular disease (MI, VTE or stroke) or breast cancer.
-
Change in the bleeding patterns is common:
-
2 in 10 women have no bleeding.
-
4 in 10 women have regular bleeding and
-
4 in 10 women have irregular bleeding.
-
-
Mood changes can occur.
Mechanism Of Action (POP)
-
Suppression of ovulation
-
up to 60% of levonorgestrel (LNG) users
-
up to 97% of desogestrel (DSG) users
-
-
Variable dampening effect on the mid-cycle peaks of LH and FSH
-
An Increase in cervical mucous viscosity
-
Reduction in the number and size of endometrial gland
Eligibility(POP)
INDICATION
-
Breastfeeding
-
Women at high risk of estrogen based contraindication
-
Older age group women
-
Women with cardiovascular/ hypertension condition
CONTRAINDICATION
-
Breast cancer
-
Undiagnosed per vaginal bleeding
-
Suspected pregnancy
-
Liver tumours
-
Acute liver disease
Starting The POP
-
Take one POP at or around the same time every day without a pill-free period.
-
POP can be started day 1 to day 5 of the menstrual period without the need of any other added contraceptive method for the next 48 hours.
-
If started at any time (pregnancy excluded) additional contraception is advised for the next 48 hours.
-
POP can be initiated immediately postpartum.
-
POP can be started immediately after a miscarriage.
Missed Pills Regime POPs
-
Traditional POPs (3-hours Window)
-
If more than 3 hrs late, ie more than 27 hrs from the last pill OR
-
Desogestrel POPs (12-hours window)
-
If more than 36 hrs late since the last pill:
-
A) The last pill should be taken as soon as remembered, if more than one pill has been missed, ONLY one pill should be taken.
-
B) The next pill should be taken at the usual time. This may mean that 2 pills are taken in one day.
-
C) Additional Contraceptive Precautions (condoms or avoidance of sex) are advised for 2 days (48hrs) after restarting the POP.
-
D) Emergency contraception is indicated if unprotected sexual intercourse occurred after the missed pill and within 48 hrs of restarting the POP.
-
Progesterone-only Injectables (Depo-Provera)
-
Intramuscular progestin are Depo medroxy progesterone acetate (DMPA) 150mg and norethisterone enanthate (NET-EN).
-
DMPA is an aqueous suspension and is in a prefilled syringe. It needs to be vigorously shaken to ensure complete suspension of the content.
-
NET-EN is a thick, oily fluid that needs to be drawn out to syringe. The ampule needs to be emerged in warm water to reduce the viscosity prior.
-
Both are administered intramuscularly into the upper outer quadrant of the buttock or in the deltoid as an alternative
-
Typical use Failure Rate is 6%
-
Use may be continued till age 50 years.
-
Concurrent use of other medications does not reduce its efficacy (including antibiotics or liver enzymes)
-
There is no association of DMPA use with mood swings, libido and headache.
-
It alters the bleeding patterns and may cause amenorrhoea amongst users after 1 year of usage. (70%)
-
There is a small association of weight gain amongst users after 6 months. However, the weight gain is mostly due to water retention.
-
There may be a small loss of bone mineral density (BMD) which will recover after discontinuation, however there is no evidence of an increase in bone fracture risk.
-
Possible delay in fertility return after 1 year of usage.
Long Term Use of Progesterone-only Injectable
-
Women using DMPA who wish to continue use should be reviewed every 2 years to assess individual situations and to discuss the benefits and potential risks
-
Women are generally advised to switch to another method at age 50.
-
There is no need to stop DMPA in long-term users as long as its use is within WHOMEC 1 or 2.
Eligibility (Progestogen-only Injectables)
INDICATION
-
Breastfeeding
-
Women at high risk of estrogen-based contraindication
-
Women of older age group
-
Women with cardiovascular / hypertension condition
-
Can be used in patients <18yrs after consideration of other methods
CONTRAINDICATION
-
Breast cancer
-
Undiagnosed per vaginal bleeding
-
Suspected pregnancy
-
Liver tumours
-
Acute liver disease
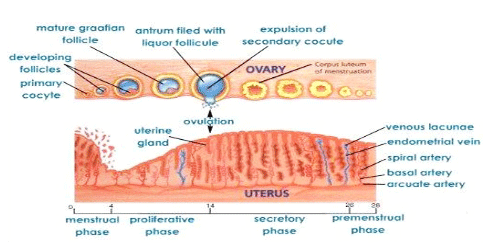
Mechanism Of Action Progesterone-only Injectable

Starting The Progestogen-only Injectables
-
For immediate protection, treatment can be started up to day-21 postpartum.
-
If started later than 21 days, additional methods of contraception are required for 7 days.
-
Treatment may be initiated immediately after surgical or medical abortion. However, if started later than 5 days post-abortion, additional methods of contraceptive are required.
-
Patients are advised to return every 12 weeks for repeat injections of DMPA.
-
If necessary, can be given 2 weeks earlier or later without the need of additional methods of contraception
References
-
Progesterone -Only Pills, Clinical Effectiveness Unit, Faculty of Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare Clinical Guidance, March 2015, Updated January 2016
-
Trussell James, Contraceptive Failure in the United States, Contraception 2011 May; 83 (5): 397-404
-
Best practice in Postpartum family Planning, Best Practice Paper No 1, June 2015, RCOG
-
OGSM basic contraception Course 2016
-
WHO Medical elilgibilty criteria updates, volume 94, Issue 3, September 2016
-
A prospective comparison of bone density in adolescent girls receiving depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (depo provera), levonogesterel (norplant) or oral contraceptive. Cromer BA et al, J Pediatr, 1996, Nov;129 (5): 671-6
Disclaimer: The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. The information is provided by OGSS Online Contraceptive Course and while we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.